Ozone disinfection is gaining attention in India as more homes and businesses explore ozone generators. While many use this technology, fewer understand the deeper science behind ozone disinfection and how it effectively eliminates pathogens. This article explores how ozone behaves in real-world settings, tackling various types of pathogens, and what science says about its effectiveness — without repeating the basic definitions.
How Ozone Interacts with Different Pathogens
Not all bacteria, viruses, or fungi react to ozone in the same way. Recent studies have shown that ozone can cause complete cell wall destruction in certain bacteria like E. coli, while in some viruses, it disrupts the lipid layer and damages RNA.
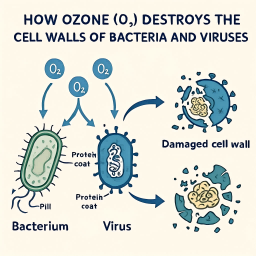
For example:
- Viruses like coronavirus are vulnerable to oxidation, especially in aerosol form.
- Fungi and mold spores are more ozone-resistant, needing longer exposure.
- Bacteria on hard surfaces are quickly neutralized — particularly useful in kitchen and bathroom cleaning.
This selective efficiency makes ozone a versatile disinfectant, especially when used under the right conditions (humidity, exposure time, surface type).
📖 For scientific background, you can refer to this peer-reviewed PubMed article on ozone’s microbial action.
Real-World Testing in Indian Conditions
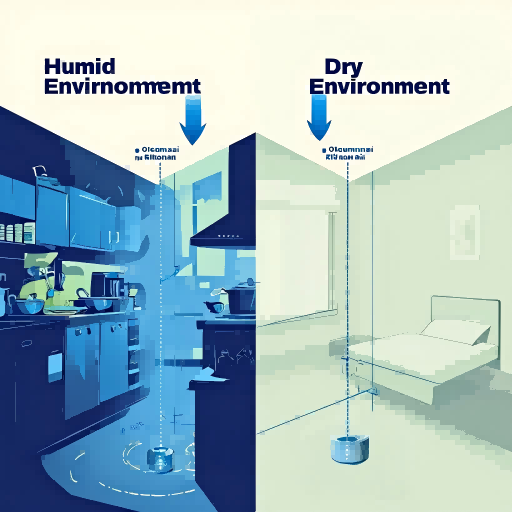
Several studies and user tests in Indian cities show different results depending on air quality and climate. In cities like Mumbai and Chennai, where humidity is high, ozone is especially effective for air purification.
In dry northern cities, ozone has shown excellent results for:
- Mold prevention in closed wardrobes
- Bathroom odor control
- Food surface sanitation, particularly for leafy vegetables and fruits
The Science of Disinfection Timing
A common misunderstanding is that “longer = better” when using ozone. However, scientific testing shows:
| Pathogen Type | Typical Ozone Exposure Needed |
|---|---|
| Surface bacteria | 10–15 minutes |
| Mold spores in air | 30–60 minutes |
| Viruses (airborne) | 15–30 minutes |
| Fruits/Vegetables | 5–10 minutes in water |
So instead of running machines for hours, smart timing and ventilation are more important. This is especially helpful in Indian homes where space and time are limited.
Effective Ozone Disinfection: Practical Benefits for Everyday Use
Ozone disinfection is a powerful and eco-friendly method widely used to eliminate harmful bacteria, viruses, and odors in water and air. Unlike traditional disinfectants, ozone works quickly by oxidizing contaminants without leaving chemical residues. For example, a mid-sized food processing factory in India implemented ozone disinfection in their water treatment system. Within weeks, they observed a significant reduction in microbial contamination and improved water clarity, which enhanced product quality and reduced chemical usage. In addition, ozone air purification in their packaging area effectively eliminated odors and airborne bacteria, creating a safer working environment. Proper use of ozone generators ensures these benefits while maintaining safety standards. This real-world case highlights how ozone disinfection provides a cost-effective, sustainable solution for industries and homes alike, supporting health and hygiene in practical ways.
Limitations: When Ozone Doesn’t Work Well
Ozone is not always perfect. It may struggle with:
- Cleaning deep cracks in surfaces unless air circulation is forced
- Disinfecting oily residues (you may still need soap)
- Removing heavy particulate pollutants (need HEPA filters)
💡 That’s why many advanced air purifiers today combine ozone + HEPA filters + UV — each plays a unique role.
Conclusion: Go Beyond the Basics
Understanding ozone goes beyond knowing “what it is.” It’s about knowing when, where, and how to use it effectively — especially in unique Indian environments.
If you’re already using or planning to buy an ozone generator, this scientific understanding helps you make smarter, safer, and more effective disinfection decisions.
