Water Treatment Technologies: Water is the essence of life, yet its availability in a clean and safe form is increasingly under threat due to population growth, industrialization, and environmental changes. Water treatment plants, water purification plants, and advanced water systems play a pivotal role in addressing these challenges, ensuring that drinking water and clean water remain accessible. This blog explores the technologies, processes, and innovations shaping the world of water processing, from traditional treatment plants to cutting-edge solutions like RAS system aquaculture and water from air generators. With a focus on logical flow and practical insights, we’ll also spotlight Vadodara, Gujarat, a city making strides in this field.
Introduction: The Importance of Water Treatment
The demand for clean water and reliable water supply has never been greater. Contaminated water sources, industrial runoff, and aging infrastructure pose significant risks to drinking water supplies. Water treatment—the process of removing impurities and contaminants from water—bridges the gap between raw water and safe drinking water. Whether it’s a water treatment plant, a sewage treatment plant, or a water refinery plant, these facilities are essential for public health, environmental protection, and sustainable development.
In this article, we’ll dive into the core components of water processing plants, explore innovative technologies like ozone injectors and air with water systems, and examine real-world applications in places like Vadodara, India. Along the way, we’ll suggest visuals to enhance understanding and ensure this content aligns with Google SEO best practices.
Suggested Image: A high-resolution photo of a serene river juxtaposed with a modern water treatment plant, captioned “From Nature to Tap: The Journey of Clean Water.”
1. The Backbone of Water Safety: Water Treatment Technologies
What Happens in a Water Treatment Plant?
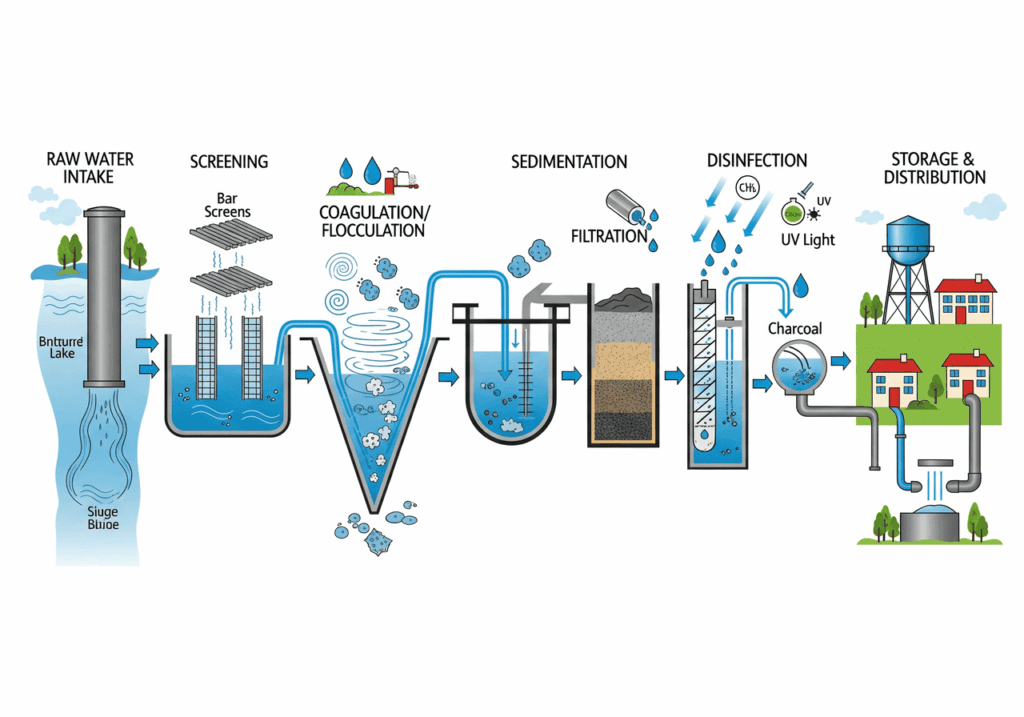
A water treatment plant transforms raw water from rivers, lakes, or groundwater into drinking water through a series of steps known as the process of water treatment plant. These steps typically include:
- Coagulation and Flocculation: Water treatment chemicals like alum bind with impurities, forming larger particles.
- Sedimentation: Heavy particles settle to the bottom.
- Filtration: Water passes through sand or gravel to remove finer particles.
- Disinfection: Technologies like ozone injectors or chlorine eliminate bacteria and viruses.
Water purification plants take this a step further, often using advanced methods like reverse osmosis or UV radiation to ensure the highest quality clean water.
Sewage Treatment Plants: Managing Wastewater
While water plants focus on potable water, sewage treatment plants handle wastewater. The sewage treatment processes—primary (physical removal of solids), secondary (biological breakdown), and tertiary (chemical polishing)—prevent pollution and recycle water for uses like irrigation or industrial cooling water.
Suggested Image: A diagram of the process water treatment stages in a treatment plant, with labels for each step.
2. Water Systems and Supply: Delivering Clean Water to Homes
The Role of Water Supply Systems
A robust water supply system ensures that treated water reaches households and businesses efficiently. These system water networks include pipelines, pumps, and reservoirs, all designed to maintain water pressure and quality. In urban areas like Vadodara, Gujarat, these systems are critical for supporting growing populations and industries.
Drinking Water Supplies and Quality
The ultimate goal of any water system is to provide drinking water supplies that meet safety standards. This involves not only treatment but also monitoring for contaminants and maintaining infrastructure to prevent leaks or recontamination.
Suggested Image: A schematic of a water supply network, showing the flow from a water processing plant to residential taps.
3. Innovations in Water Technology
RAS System Aquaculture: Sustainable Fish Farming
The RAS system aquaculture (Recirculating Aquaculture System) is a game-changer for water use in agriculture. By recycling water through filtration and disinfection, RAS reduces waste and ensures a steady supply of clean water for fish farming. This technology integrates water treatment system processes like biofiltration and oxygenation, making it both eco-friendly and efficient.
Water from Air Generators: A New Frontier
In arid regions or emergencies, water from air generators offer a revolutionary solution. These devices extract moisture from air with water, condensing it into drinking water. Paired with water plant purification techniques, they provide a decentralized approach to water water supply.
Ozone Injectors: Advanced Disinfection
The ozone injector is increasingly popular in water treatment plants for its ability to disinfect without leaving chemical residues. It’s a key tool in producing high-quality water drinking water.
Suggested Image: A close-up of an ozone injector in action, with a caption explaining its role in water processing.
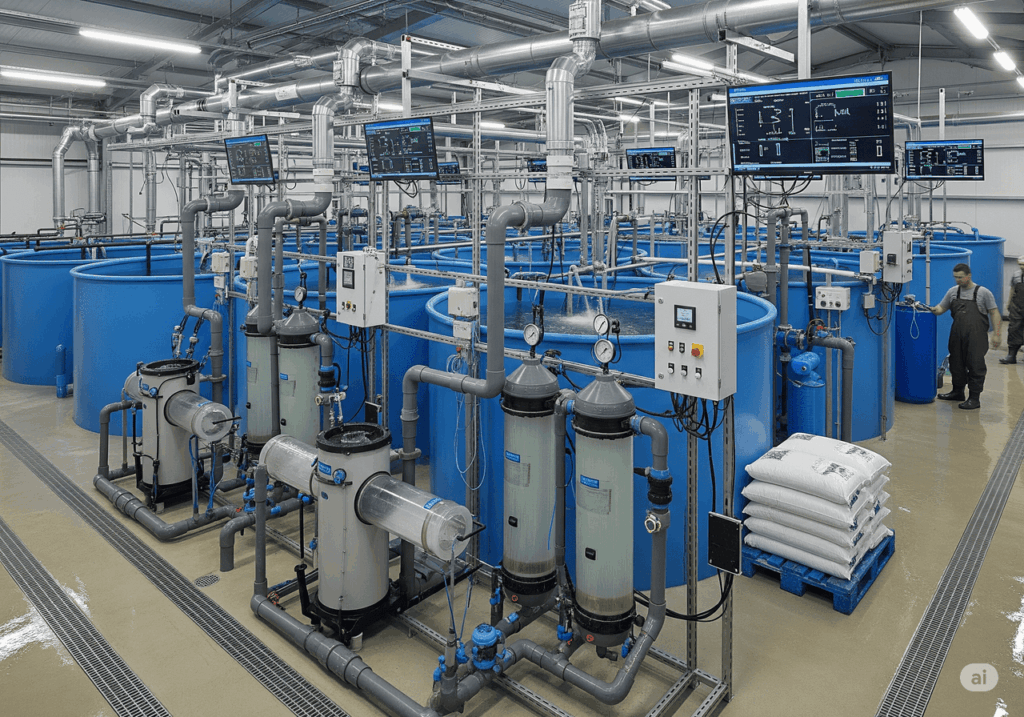
4. Case Study: Water Treatment in Vadodara, India
Vadodara, India, located in Gujarat, is a hub of industrial and urban development, making water treatment a priority. The city has invested in modern treatment plants and sewage treatment plant types to manage its water resources effectively. For instance:
- Water Processing Plants: Facilities here use membrane filtration to treat river water.
- Sewage Treatment: Biological reactors reduce pollution in the Vishwamitri River.
- Innovative Projects: Local adoption of RAS system aquaculture supports sustainable food production.
These efforts showcase how water and water treatment can coexist with urban growth.
Suggested Image: A photo of a water treatment plant in Vadodara, Gujarat, with modern equipment in the foreground.
5. The Future of Water Treatment
The future of water treatment for plants and human consumption lies in sustainability and technology. Trends include:
- Smart Water Systems: IoT-enabled monitoring for real-time water quality checks.
- Eco-Friendly Chemicals: Safer water treatment chemicals with minimal environmental impact.
- Decentralized Solutions: Wider use of water from air generators and small-scale plant for water purification.
These advancements promise to enhance drinking water manufacturer capabilities and ensure a steady manufacture of mineral water globally.
Suggested Image: A conceptual illustration of a futuristic water treatment system process, featuring smart sensors and renewable energy sources.
6. Conclusion: Securing Clean Water for All
From water water treatment plants to innovative water of air technologies, the field of water processing is evolving to meet modern challenges. Whether it’s ensuring water clean water through traditional treatment plants or pioneering new methods in places like Vadodara, India, the goal remains the same: a sustainable supply of drinking water for all.
By integrating technologies like RAS system aquaculture, ozone injectors, and water from air generators, we can protect our most precious resource—water—and build a healthier, more resilient future.
Suggested Image: A global map highlighting regions advancing water treatment water treatment, with a focus on Vadodara.
